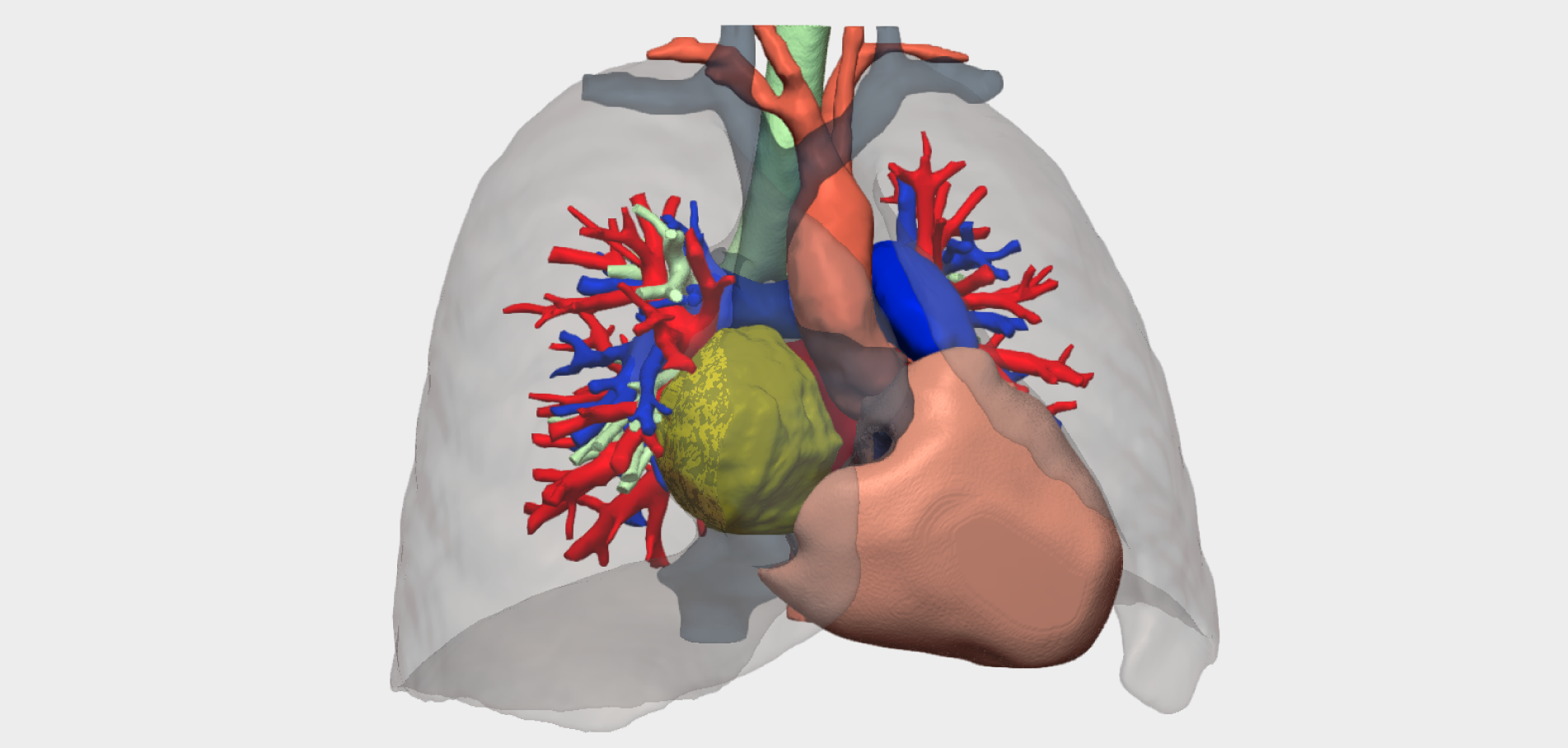
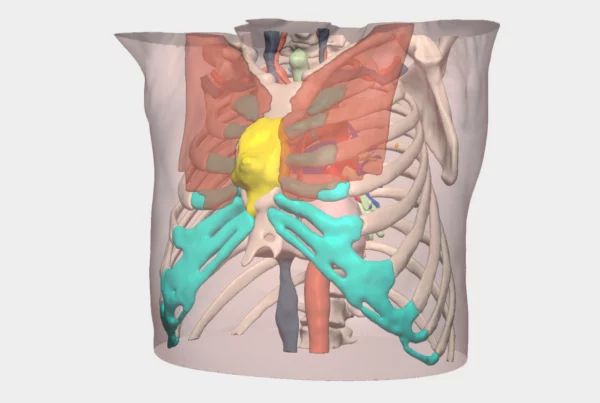
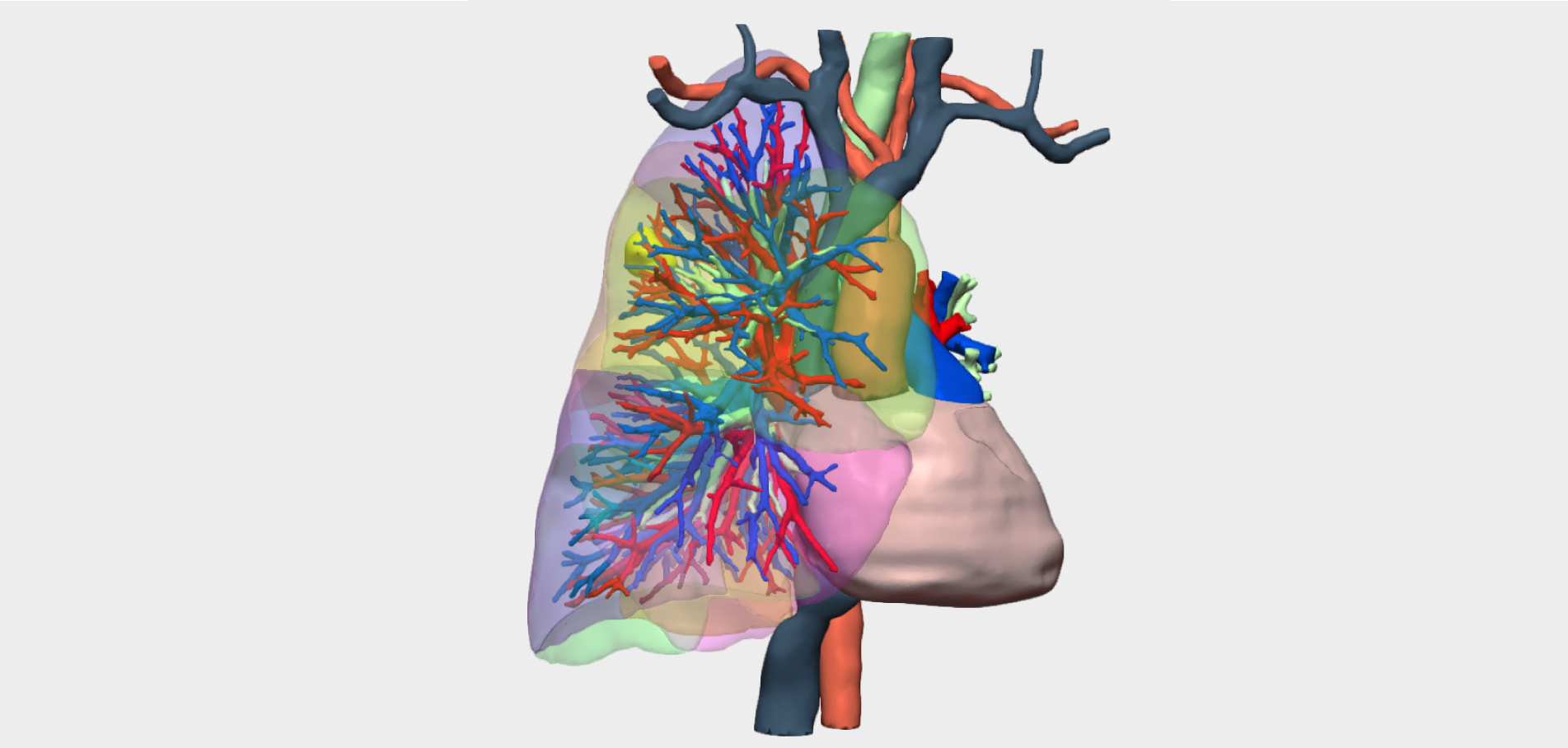
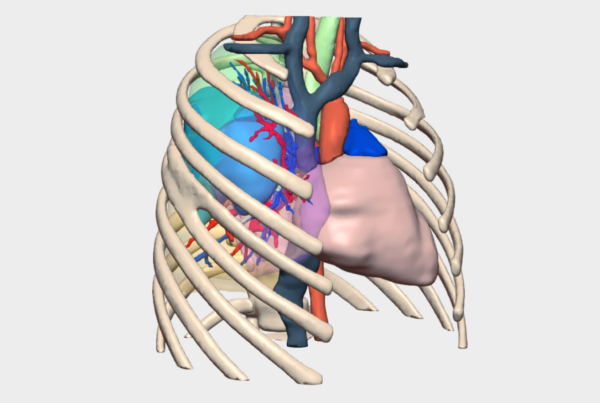
”Planning with both the virtual and physical 3D models enabled a more effective surgical strategy. It allowed us to previsualise venous cannulation sites and rhabdomyoma attachment points, anticipating the different options for cardiac resection and reconstruction depending on intraoperative findings
Dr. Antonio Jiménez AceitunaConsultant Cardiac Surgeon, Hospital Universitario Virgen de la Arrixaca
Clinical Case
On physical examination, the patient was asymptomatic. However, during the most recent cardiology follow-up, a rounded, well-defined mass measuring 56 × 54 mm, with no internal flow, was identified. The lesion did not move with the cardiac cycle and appeared to be located anterior to the right atrium (RA). No valvular involvement or impairment of right atrial or right ventricular (RV) filling was observed.
To further characterise the lesion, a CT angiography was performed, revealing the following findings:
-
-
A large tumour mass with soft-tissue density and smooth contours, occupying almost the entire right atrium
-
Mass effect on the interatrial septum, displacing it towards the left atrium (LA)
-
Approximate dimensions: 61 × 51 × 62 mm (transverse × anteroposterior × craniocaudal)
-
No evidence of pulmonary parenchymal infiltration
-
No pleural or pericardial effusion
-
No significant mediastinal, hilar or axillary lymphadenopathy
-
Normal calibre of the thoracic aorta and pulmonary artery
-
No signs of pulmonary thromboembolism
-
Two non-specific ground-glass opacities in the right lower lobe, possibly of inflammatory or infectious origin
-
Multiple bilateral pulmonary nodules (>10), measuring 2–3 mm, randomly distributed and non-specific
-
On upper abdominal slices, a hypodense lesion in hepatic segment IVB, consistent with a lipoma.
-
Based on these findings, surgical resection of the cardiac mass was indicated.
Surgical Planning with the 3D Model
Preoperative planning using both virtual and physical 3D models enabled a more accurate and safer surgical strategy. The models allowed previsualisation of venous cannulation sites and tumour attachment points, facilitating anticipation of different resection and potential cardiac reconstruction scenarios depending on intraoperative findings.
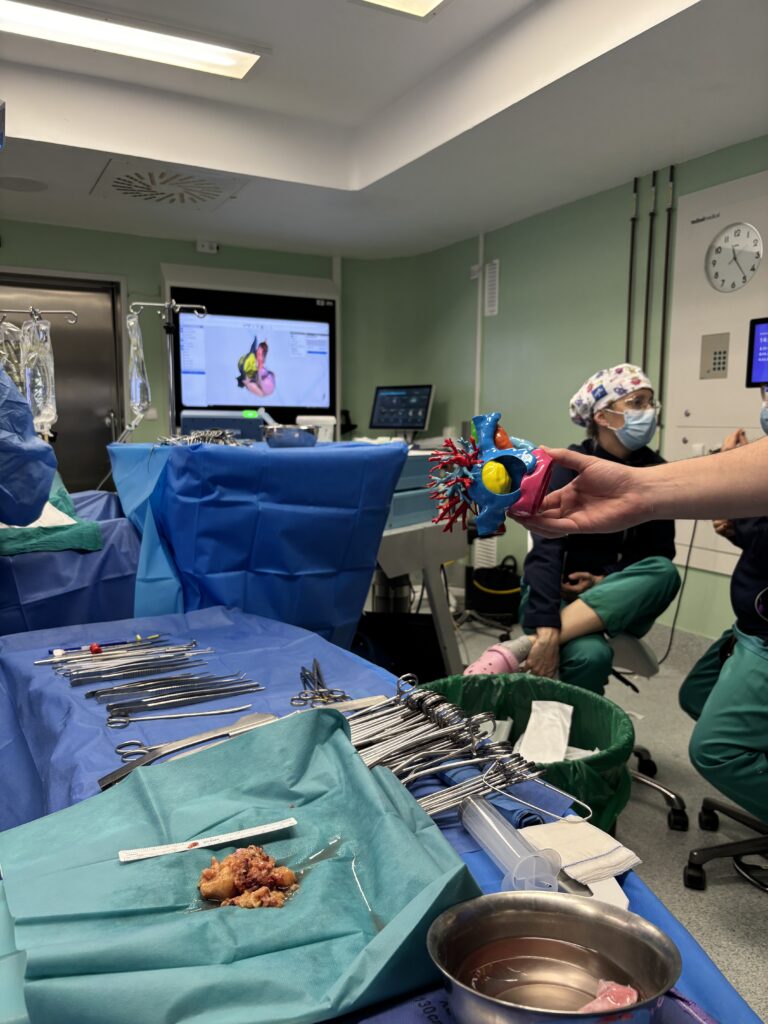
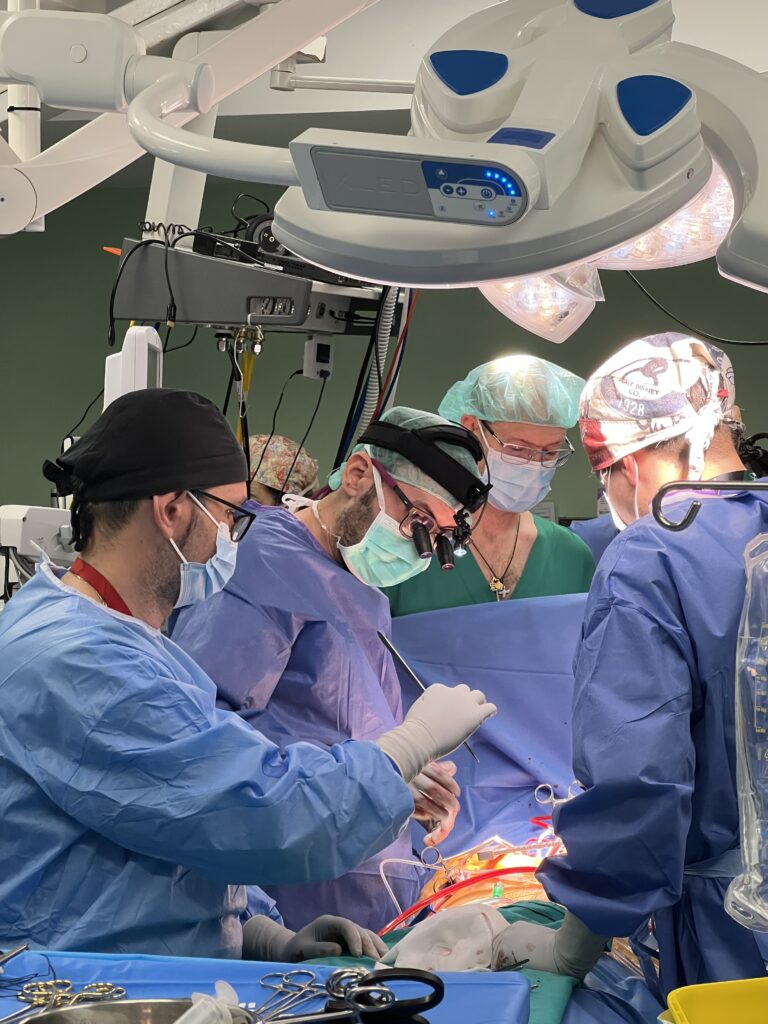
Surgical Approach and Outcomes
The procedure was performed by Dr Juan Miguel Aguilar and Dr José María Arribas, with the collaboration of Dr Antonio Jiménez Aceituna and Dr Carlos Moreno, consultant cardiac surgeons at Hospital Universitario Virgen de la Arrixaca.
Surgery was carried out via median sternotomy under cardiopulmonary bypass, with a CPB time of 65 minutes and an aortic cross-clamp time of 50 minutes. Complete excision of the mass was achieved without the need for resection of the free atrial wall or the interatrial septum.
No intraoperative or immediate postoperative complications were observed. At 48 hours post-surgery, the patient showed a favourable clinical course.
Surgical Team Conclusions
The use of 3D model–assisted surgical planning significantly facilitated tumour resection by allowing preoperative anticipation of different surgical scenarios. The high anatomical fidelity of the models ensured close alignment with intraoperative reality, supporting safer decision-making and optimal surgical outcomes.
¡Follow us on social media to stay up to date with our latest clinical cases and innovations!